Data Privacy and Security Concerns in AI: Should You Be Worried?
The rapid integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) into numerous sectors has opened significant opportunities but also introduced unique data privacy and security challenges. As AI technology becomes more prevalent in industries, handling vast amounts of sensitive personal and business data becomes increasingly critical. AI systems, including machine learning models, rely on data to learn, make predictions, and inform decisions. However, the vast amounts of data they process can expose sensitive information, leading to privacy risks and security vulnerabilities.
What is Data Privacy in AI?
Data privacy in AI refers to the protection of sensitive data used and generated by AI systems. These systems require large datasets for training machine learning models, and these datasets often contain personal information. Mishandling of this data, whether through data breaches, unauthorised access, or misuse, can lead to serious privacy violations. AI systems may inadvertently expose sensitive information, whether it’s through data mining or profiling individuals based on their behaviour or personal attributes. Hence, ensuring data privacy means safeguarding against both intentional and unintentional breaches of private information.
Why Data Privacy and Security are Crucial in AI
AI systems are rapidly transforming industries and the stakes for data privacy and security have never been higher. These technologies actively process vast amounts of personal and sensitive information, making them prime targets for malicious actors. Protecting user data is an immediate imperative. The misuse or theft of this data can have severe consequences, such as financial loss, reputation damage, or even legal action. Moreover, AI systems often operate with a significant degree of autonomy, which means that privacy violations can happen without human oversight, further complicating data security efforts.
Real-world examples, such as AI-powered healthcare systems and financial institutions, showcase the potential risks. For instance, AI used in healthcare may store patient information, making it vulnerable to breaches. Similarly, AI-driven financial systems that rely on consumer data can inadvertently expose financial details if not adequately protected.
Key Data Privacy and Security Risks in AI
AI systems introduce unique security risks due to the sheer volume and sensitivity of data they process. Understanding these risks is essential for developing strategies to mitigate them.
Data Breaches in AI Systems
AI systems that handle large volumes of sensitive data are prime targets for cybercriminals. A data breach occurs when unauthorised individuals gain access to protected data. In AI systems, breaches often happen during the model training process, where sensitive personal data may be exposed. For example, the American Medical Collection Agency (AMCA) data breach of 2019, a major data breach in an AI-powered health system, exposed millions of patients’ records, leading to privacy violations and exposure of financial details.
To mitigate the risks, organisations need to ensure that AI models are trained on encrypted datasets and that access to sensitive information is tightly controlled. Strong encryption and robust access controls are fundamental in safeguarding data.
Adversarial Attacks on AI Systems
Adversarial attacks are deliberate attempts to manipulate AI systems to produce incorrect results. In the context of AI and cybersecurity, these attacks are designed to exploit vulnerabilities in AI algorithms. For instance, adversarial machine learning can manipulate input data to deceive AI models, causing them to make wrong predictions or decisions. Such attacks can have severe consequences, especially in sectors like finance and cybersecurity, where AI systems are used for fraud detection or risk analysis.
Defending against adversarial attacks involves continuous model testing and the implementation of techniques like adversarial training, which exposes AI models to potential attacks during development to improve their resilience.
AI and Privacy Violations
AI technologies can lead to privacy violations in several ways. First, AI systems can “mine” vast amounts of personal data, sometimes without explicit consent from individuals. Additionally, AI algorithms can be used for profiling individuals, which may violate privacy laws in some states or nations, especially when personal data is used for purposes beyond what was initially intended.
For example, AI-powered recommendation engines in e-commerce might collect and process user data to create personalised shopping experiences. However, if this data is used to manipulate user choices without their knowledge, it can lead to privacy violations. To avoid such issues, organisations must ensure that data collection practices are transparent, and that users have control over the data that is collected and how it is used.
Ethical Issues in AI Data Security
The ethical implications of AI in data security are wide-ranging. One major concern is algorithmic bias. AI models can inherit biases from the data they are trained on, leading to discriminatory outcomes. For instance, if an AI system used in recruitment is trained on biased data, it may inadvertently discriminate against certain demographic groups. Similarly, AI systems can perpetuate societal inequalities if not carefully monitored.
Another ethical concern is the responsible use of AI to handle personal data. AI should be developed with fairness and transparency in mind, ensuring that individuals’ rights to privacy are respected. Organisations need to assess the ethical impact of AI systems and ensure they operate within established norms of privacy protection and fairness.
Best Practices for Securing AI Systems and Protecting Data Privacy
Given the data privacy and security risks associated with AI, it is essential to adopt best practices for securing AI systems and safeguarding sensitive data.
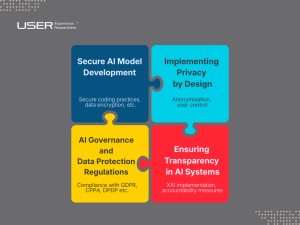
Secure AI Model Development
When developing AI systems, security should be a priority from the outset. Secure coding practices, data encryption, and the use of privacy-preserving techniques like federated learning are essential to protect sensitive information. Federated learning, for instance, allows AI models to be trained on data locally, preventing sensitive data from being shared across centralised systems.
Additionally, using techniques such as differential privacy can help ensure that AI models do not inadvertently reveal personal information when making predictions.
Implementing Privacy by Design
Privacy by design is a concept that advocates for privacy considerations to be embedded in every phase of AI development. From the initial design stage to deployment, AI systems should incorporate privacy and security features that protect users’ data. This includes ensuring that data is anonymised, encrypted, and that users have control over their personal information.
AI Governance and Data Protection Regulations
AI governance is crucial for ensuring that organisations comply with data privacy regulations. Laws such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) provide frameworks that help organisations handle data responsibly. These regulations emphasise the importance of data protection, user consent, and transparency. AI practitioners must be well-versed in these laws and work proactively to ensure that AI systems are designed and operated within these legal frameworks.
Ensuring Transparency in AI Systems
Transparency is key to building trust in AI systems. AI systems should be explainable, meaning that the decision-making processes of AI models are understandable to users and stakeholders. Explainable AI (XAI) allows organisations to demonstrate how AI systems process personal data and make decisions, which helps foster accountability and trust. By prioritising transparency, organisations can mitigate privacy concerns and provide users with more control over their data.
Case Studies: AI Data Privacy and Security Challenges
Case Study 1: Data Breach in AI-powered Health Systems
In 2019, a large AI-powered health system experienced a data breach that exposed millions of patients’ sensitive medical records. The breach occurred due to inadequate data protection practices during the model training process, allowing unauthorised access to sensitive data. This breach had significant consequences, including financial penalties and loss of trust among patients. Had the organisation employed stronger encryption and access controls, the breach could have been prevented.
Case Study 2: AI and Privacy Violations in Financial Institutions
In a recent case, an AI system used by a financial institution to provide personalised investment advice led to privacy violations. The AI system inadvertently processed user data beyond the scope of the initial consent, exposing sensitive financial information. This case highlights the importance of ensuring that AI systems are transparent in their data handling practices and that users are given clear control over their personal information.
Future Trends in AI Privacy and Security
The Role of AI in Enhancing Cybersecurity
While AI poses privacy and security risks, it is also being used to enhance cybersecurity. AI-powered threat detection systems can identify and respond to cyber threats faster than traditional methods, helping organisations protect their data and systems. However, as AI is integrated into cybersecurity, new challenges, such as adversarial attacks on security systems, must be addressed.
The Evolving Landscape of AI Data Protection Laws
As AI technologies continue to evolve, so will the legal frameworks governing data protection. Governments around the world are likely to introduce new regulations to address the growing concerns about AI’s impact on privacy and security. Organisations will need to stay informed and adapt to these changes to remain compliant.
Conclusion: The Need for Proactive AI Data Privacy and Security Measures
AI presents both opportunities and challenges when it comes to data privacy and security. While it can enhance efficiency and decision-making, AI also introduces significant risks, including data breaches, adversarial attacks, and privacy violations. Organisations must adopt proactive measures to secure their AI systems, protect sensitive data, and comply with data protection regulations. By implementing best practices, prioritising transparency, and adhering to ethical standards, businesses can ensure that AI technologies are used responsibly and securely.
About User Experience Researchers
At the forefront of innovation, User Experience Researchers is committed to elevating the user journey and value across all touchpoints. Our expertise range across UX consulting, digital transformation, and IT staffing solutions – fulfilling crucial strategy, technology, and talent needs. We are committed to drive progress in sustainable ways. Unlock your full potential with digital by partnering with us.
FAQ
- What are the main privacy concerns associated with AI?
AI systems often process vast amounts of personal data, leading to risks such as data breaches, unauthorised access, and profiling. Privacy violations can occur if data is mishandled or used without explicit consent.
- How can adversarial attacks affect AI systems?
Adversarial attacks manipulate AI models by introducing subtle changes to input data, causing incorrect predictions or decisions. These attacks can undermine AI systems used in critical areas like cybersecurity and finance.
- What are some examples of AI-related data breaches?
AI-powered health systems and financial institutions have experienced breaches where sensitive personal data was exposed due to inadequate security measures or system vulnerabilities.
- What does “privacy by design” mean in the context of AI?
“Privacy by design” refers to embedding privacy considerations into every stage of AI development, ensuring that data protection and security are prioritised from the outset.
- How can AI systems be developed securely to protect data privacy?
Secure AI development involves using encryption, federated learning, differential privacy, and secure coding practices to protect sensitive data during model training and deployment.
- What are the ethical challenges of AI in relation to data security?
AI can perpetuate biases and discrimination if not developed with fairness in mind. Ethical concerns also include the responsible use of AI in managing personal data and ensuring transparency in decision-making.
- How can organisations ensure compliance with data privacy regulations in AI?
Organisations should stay informed about data protection laws such as GDPR and CCPA, implement privacy by design, and ensure that AI systems operate transparently and securely.
- What role does AI play in cybersecurity?
AI enhances cybersecurity by enabling faster detection and response to threats. However, AI-driven systems themselves must be protected from adversarial attacks.
- What is explainable AI, and how does it contribute to data privacy?
Explainable AI (XAI) ensures that AI decision-making processes are transparent and understandable, fostering trust and accountability, which are essential for data privacy.
- How can AI practitioners stay updated on evolving data protection laws?
AI practitioners can stay updated by regularly reviewing regulatory updates, participating in industry forums, and ensuring their systems are compliant with local and international data protection laws.